
However, in reality, such a clean-cut distinction does not always exist. In theory, it may seem relatively easier to detect where physics leaves off and mathematics picks up. The central difference between physics and mathematics is that ultimately physics is concerned with descriptions of the material world whereas mathematics is focused on abstract logical patterns that may extend beyond the real world.īecause physics concentrates on the material world, it tests its theories through the process known as observation or experimentation.

A great many of physics' definitions, models, and theories are expressed using mathematical symbols and formulas. The specific ways in which they apply to energy (hence, physics) are often referred to as the "laws of physics."īecause each of the other natural sciences biology, chemistry, geology, material science, medicine, engineering, and others, work with systems which adhere to the laws of physics, physics is often referred to as the "fundamental science."įor an example of how the laws of physics apply to all of the other sciences, consider that chemistry, the science of matter which studies atoms and molecules, complies with the theories of quantum mechanics, thermodynamics, and electromagnetism in order to produce chemical compounds.Īs a whole, physics is closely related to mathematics, for it provides the logical structure in which physical laws may be formulated and their predictions quantified. Because of this overlap, phenomena studied in physics (conservation of energy for example) are common to all material systems.
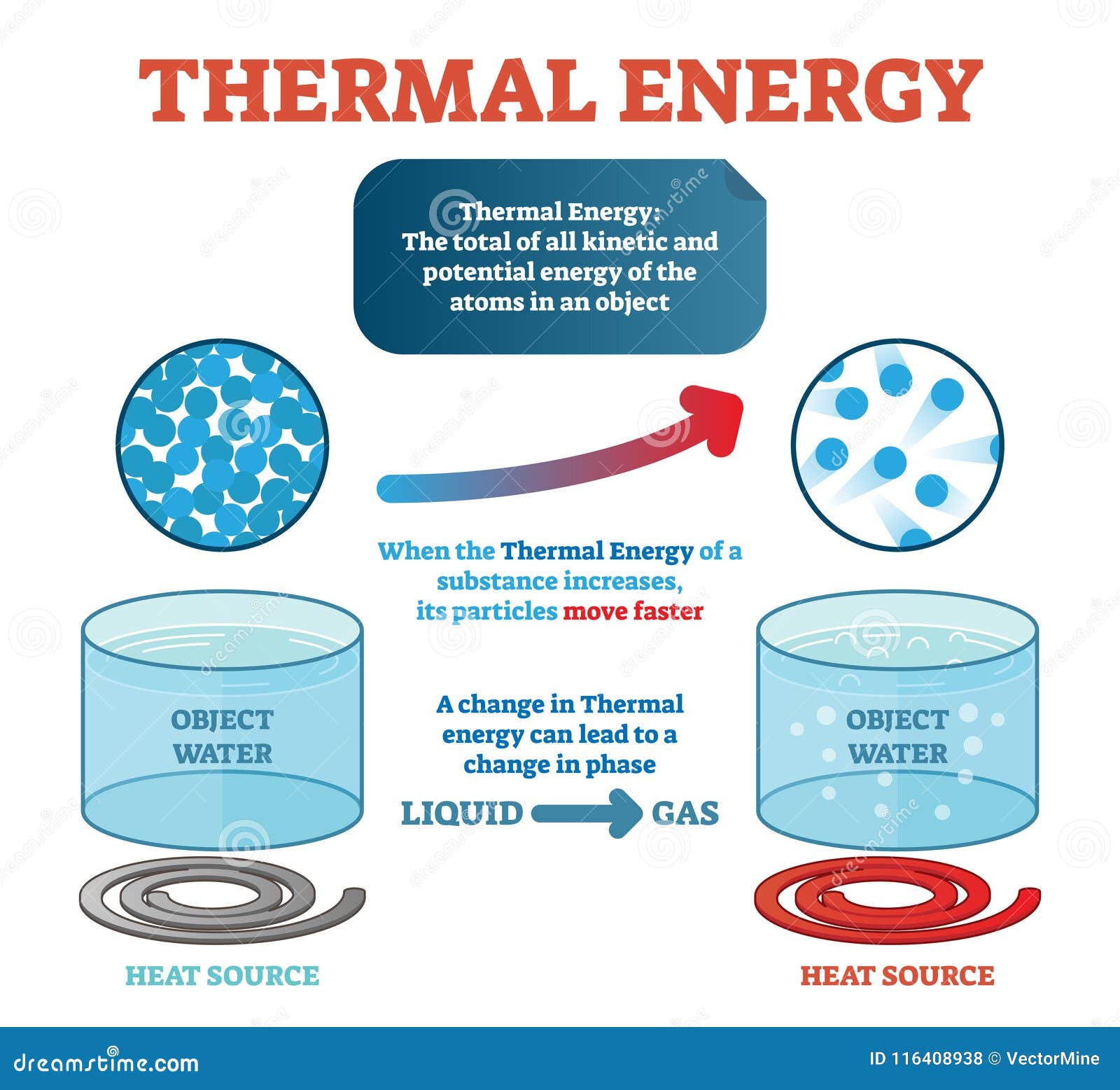
To understand the fundamental principles of the universe, physics utilizes many workings from the other natural sciences. Physics, as opposed to natural philosophy (with which it was grouped until the 19 th century), relies upon scientific methods in order to describe the natural world. Quite often, physics concentrates upon the forces having an impact upon matter, that is, gravitation, heat, light, magnetism, electricity, and others.īecause physics utilizes elements of other branches of sciences, biology and chemistry for example, it has the reputation of being more complicated than other sciences. The science in which matter and energy are studied both separately and in combination with one another.Īnd a more detailed working definition of physics may be: The science of nature, or that which pertains to natural objects, which deals with the laws and properties of matter and the forces which act upon them. To better understand this connection, it helps to refer to a solid working definition of physics. When learning about and discussing physics, we focus heavily on energy, the core element of the science.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
